Noticing your gums receding can be a cause for concern, in more ways than one. Left untreated, as the margin of the gum tissue pulls back and exposes your tooth, you can end up dealing with a number of dental issues including tooth sensitivity, infection and even tooth loss. In this guide, we will explain everything you need to know about gum recession – from causes to treatments and prevention, so you can take the necessary steps to protect your smile.
What is Gum Recession?
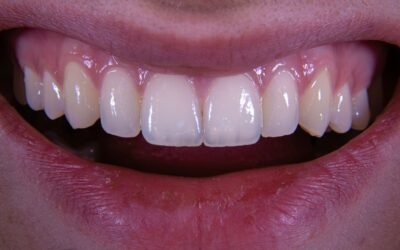
Receding gums, known clinically as gingival recession, is the process of your gum tissue surrounding your teeth wearing away or pulling back, over time exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. This exposure can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, decay and even tooth loss. Your gums serve as a vital protective barrier for your teeth, and when they recede, this protection is compromised. Gum recession can affect one tooth at a time or several at once and tends to occur slowly, going unnoticed until the more advanced gum recession stages.
What are the Signs of Receding Gums?
Early detection of gum recession is crucial for preventing further damage to your oral health. Some of the most common receding gums symptoms include:
- Tooth sensitivity, especially to hot, cold or sweet food and drink
- Visible tooth roots where gums pull away to reveal the yellowish root surface
- Teeth that appear longer than usual
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Swollen or red gums which can indicate inflammation or infection
What Causes Receding Gums?
There are a number of reasons why your gum line can begin to wear away and recede. The actual cause for why this might be happening to you is actually likely to be a combination of factors which includes:
- Poor oral hygiene leading to plaque and tartar buildup
- Brushing too aggressively or using a hard-bristled toothbrush
- Gum disease, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, which causes tissue breakdown
- Genetics – some people are more prone to gum issues
- Smoking or the use of tobacco products
- Hormonal changes, particularly in women during pregnancy or menopause
- Misaligned teeth or teeth grinding, which puts extra pressure on gums
Understanding the cause of gum recession is key to choosing the right dental treatment and preventing further damage.
Stages of Gum Recession
Receding gums typically progress through three distinct stages, which will help your dentist assess the extent of the damage and determine what sort of treatment is required to alleviate the symptoms.
- Early stage – Mild gum recession with no major symptoms except slight sensitivity
- Moderate stage – Noticeable root exposure, increased sensitivity and possible inflammation
- Advanced stage – Significant gum loss, loose teeth and possible bone involvement
Regular dental examinations and general check-ups can help identify gum recession early and manage its progression effectively.
Can You Reverse Receding Gums?
Patients suffering from a receding gum line and its associated symptoms will often ask whether or not it is possible to reverse the deterioration and help their gums grow back. Unfortunately, gum tissue does not regenerate in the way other types of tissue do. Once it has receded, it will not grow back naturally. However, that doesn’t mean you are out of options and will have to live with exposed gums forever. There are both surgical and non-surgical treatments that can restore the appearance and health of your gums.
Receding Gum Treatment Options
Professional Dental Treatments for Gum Recession
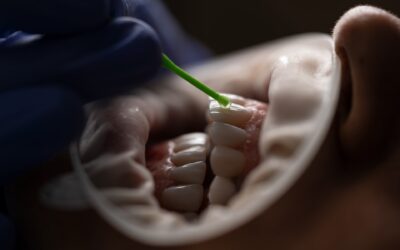
Treatment for receding gums varies depending on the severity and underlying cause. Professional dental treatments often begin with non-surgical procedures such as scaling and root planing, which remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line. These deep cleanings help reduce inflammation and allow the gums to reattach to the tooth.
In more severe cases, surgical solutions such as gum grafting may be recommended. This involves transferring tissue from another area of the mouth to cover the exposed root, reducing sensitivity and protecting against further recession.
Reverse Receding Gums at Home
While professional care is essential, there are also at-home strategies that can complement these treatments. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and practising gentle brushing techniques can prevent further irritation.
Antibacterial mouthwashes can help reduce plaque and promote healthier gums, while specific toothpastes designed for sensitivity may alleviate discomfort. Natural remedies such as oil pulling with coconut oil or rinsing with salt water may offer additional benefits, although they should be used cautiously and not as a substitute for actual dental treatment.
A consistent oral hygiene routine, paired with regular dental check-ups, is crucial to maintaining progress and preventing the return of receding gum issues.
When to See a Dentist for Receding Gums?
If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned earlier, especially tooth sensitivity, visible roots or bleeding gums, it’s time to see a dentist. Early intervention can mean the difference between preserving and losing a tooth.
Conclusion
Gum recession is a common but serious dental issue that can lead to sensitivity, infection and even tooth loss if left untreated. Fortunately, with early detection and the right treatment, it can be managed effectively. Reach out to your local dentist to better understand the condition and get the right treatment to help you maintain a healthy, confident smile.