In the realm of dental care, advancements in materials and techniques have provided patients with more options than ever before when it comes to restoring teeth. Two popular choices for repairing dental imperfections are white fillings and composite bonding. While they share similarities in their application and aesthetic benefits, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for various dental needs.
White Fillings
White fillings, also known as composite fillings or tooth-coloured fillings, are primarily used to repair cavities caused by decay. They are composed of a mixture of plastic resin and small glass particles, which give them their natural appearance that blends seamlessly with the surrounding teeth. Here are some key features of white fillings:
- Functionality: White fillings are designed to restore the structural integrity of a tooth after decay removal. They are durable and can withstand moderate pressure from chewing.
- Application: The process of placing a white filling involves removing the decayed portion of the tooth, cleaning the affected area, and then filling it with the composite material. The filling is then shaped to match the natural contours of the tooth and hardened with a special light.
- Benefits: Beyond their aesthetic appeal, white fillings bond directly to the tooth enamel, providing additional support and insulation against temperature changes.
- Durability: With proper care and regular dental check-ups, white fillings can last for many years, making them a reliable choice for restoring decayed teeth.
Composite Bonding
Composite bonding, often referred to simply as dental bonding, serves a different purpose compared to white fillings. It involves the application of a tooth-coloured composite resin to repair chipped, cracked, or discoloured teeth, as well as to close gaps between teeth. Here’s what sets composite bonding apart:
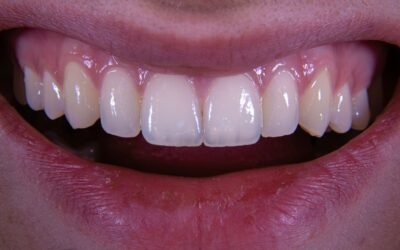
- Cosmetic Enhancement: While bonding can restore small cavities, its primary function is cosmetic improvement. Dentists use bonding to reshape teeth, repair minor imperfections, and enhance overall smile aesthetics.
- Procedure: Unlike fillings, bonding typically requires minimal tooth preparation. The composite resin is applied directly onto the tooth’s surface, sculpted into the desired shape, and then hardened with a curing light.
- Versatility: Bonding is versatile in addressing various aesthetic concerns, including altering tooth shape, improving colour, and filling in gaps between teeth. It can also be used to cover exposed root surfaces in cases of gum recession.
- Longevity: While bonding is durable, it may not last as long as traditional fillings. Factors such as oral hygiene practices, biting forces, and dietary habits can impact its lifespan.
Choosing Between White Fillings & Composite Bonding
When deciding between white fillings and composite bonding, several factors come into play:
- Nature of the Problem: For cavities caused by decay, white fillings are the appropriate choice to restore tooth structure and prevent further damage. For cosmetic enhancements and minor repairs, bonding offers a versatile solution.
- Location of the Tooth: Teeth subjected to significant biting forces may benefit more from the strength of white fillings, whereas bonding is ideal for teeth primarily needing aesthetic improvements.
Consulting with a dentist is crucial to determine the best option based on individual dental needs and goals. Both white fillings and composite bonding provide effective solutions for restoring dental health and enhancing smile aesthetics, contributing to overall oral well-being and confidence in one’s appearance.